Solve for x the polygons in each pair are similar – Embarking on the exploration of solving for x in similar polygons, this discourse unveils the intricate relationship between geometric shapes, ratios, and proportions. Delving into the realm of similar polygons, we uncover their unique characteristics, practical applications, and the systematic process of solving for x, empowering individuals with a valuable tool for tackling real-world problems.
Similar polygons, mirroring each other in shape but not necessarily in size, exhibit remarkable properties that facilitate the determination of unknown dimensions. By harnessing these properties and employing a step-by-step approach, we can skillfully solve for x, unlocking a treasure trove of insights into the fascinating world of geometry.
Definitions and Concepts: Solve For X The Polygons In Each Pair Are Similar
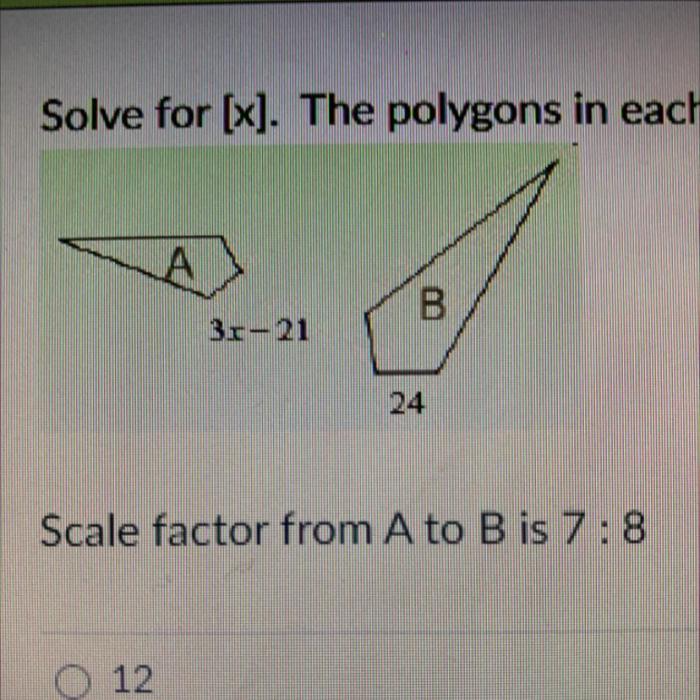
In geometry, similar polygons are polygons that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. The corresponding sides of similar polygons are proportional, meaning they have the same ratio. For example, if two squares have side lengths of 4 cm and 8 cm, respectively, they are similar because their sides are in the ratio of 1:2.
Solving for x
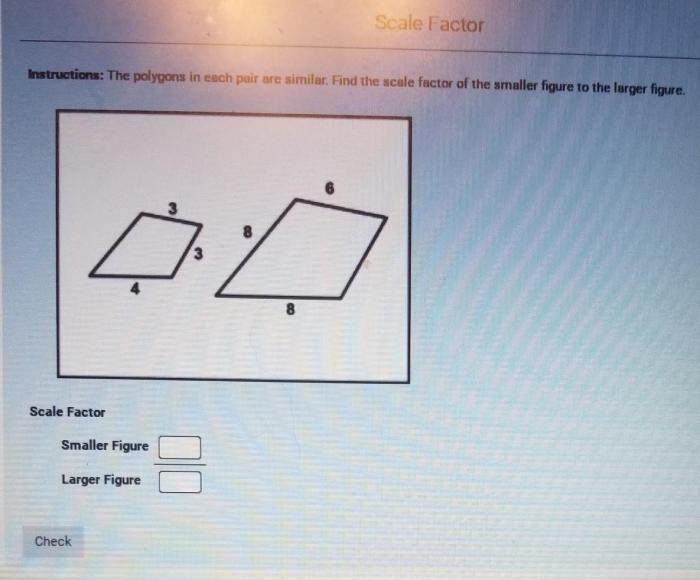
To solve for x in similar polygons, we can use the following steps:
- Identify the corresponding sides of the similar polygons.
- Set up a proportion between the corresponding sides.
- Cross-multiply to solve for x.
Applications
Solving for x in similar polygons has many practical applications, including:
- Architecture: Determining the dimensions of a building or structure based on a scale model.
- Engineering: Calculating the forces and stresses on a bridge or other structure.
- Art: Creating proportional drawings or paintings.
Properties of Similar Polygons
The following properties of similar polygons are relevant to solving for x:
- Corresponding angles are congruent.
- Corresponding sides are proportional.
- The ratio of the areas of similar polygons is equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
Examples and Practice Problems
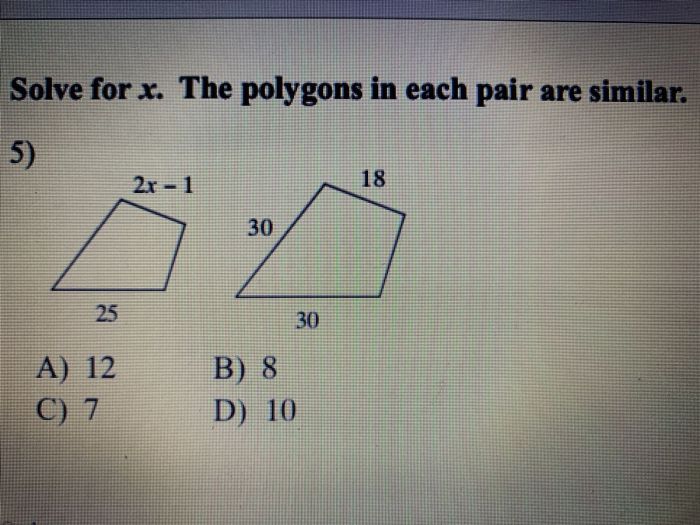
| Type of Polygon | Corresponding Sides | Proportion | Solution for x |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squares | a : b | a/b = x/b | x = a |
| Rectangles | a : b | a/b = x/c | x = (a/b)
|
| Triangles | a : b | a/b = x/c | x = (a/b)
|
Practice Problems:
- Two similar triangles have side lengths of 3 cm and 5 cm. If the shorter side of the second triangle is 6 cm, find the length of the longer side.
- A rectangular garden has a length of 10 m and a width of 5 m. A similar garden has a length of 15 m. What is the width of the second garden?
Advanced Concepts
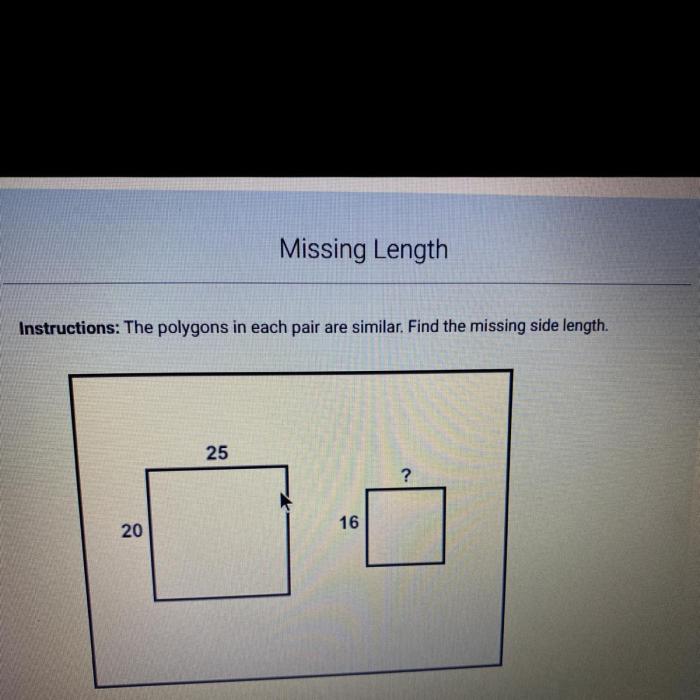
Advanced concepts related to solving for x in similar polygons include:
- Scale factors: The ratio of the corresponding sides of similar polygons.
- Ratios: The relationship between the corresponding sides of similar polygons.
These concepts are applied in more complex problems, such as:
- Determining the dimensions of a three-dimensional object based on a two-dimensional drawing.
- Calculating the forces and stresses on a complex structure.
Top FAQs
What is the definition of similar polygons?
Similar polygons are polygons that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. They have corresponding angles that are equal in measure and corresponding sides that are proportional.
How do I solve for x in similar polygons?
To solve for x in similar polygons, you can use the following steps: 1. Identify the corresponding sides of the similar polygons. 2. Set up a proportion using the corresponding sides. 3. Cross-multiply to solve for x.
What are some real-world applications of solving for x in similar polygons?
Solving for x in similar polygons has many real-world applications, such as: – Architecture: Determining the dimensions of a building or structure based on a scale model. – Engineering: Calculating the forces acting on a bridge or other structure. – Surveying: Determining the distance to an object using similar triangles.