Introducing the Respiratory System Worksheet Answer Key, a comprehensive resource meticulously crafted to empower learners with a profound understanding of the intricacies of the respiratory system. This authoritative guide embarks on an illuminating journey, deciphering the complexities of respiration, unveiling the anatomy of the respiratory apparatus, and unraveling the mechanisms that govern respiratory physiology.
Delve into the fascinating world of respiration, where the symphony of inhalation and exhalation sustains life. Discover the intricate interplay between the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, orchestrating the rhythmic expansion and contraction of the lungs. Witness the vital exchange of gases between the delicate alveoli and the bloodstream, a process that nourishes every cell in our bodies.
Definition and Overview
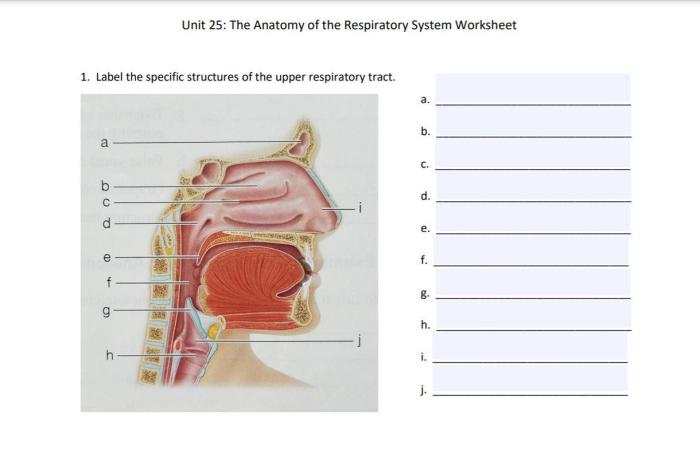
The respiratory system is a complex network of organs and tissues that work together to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. It enables the uptake of oxygen (O2) from the air and the release of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste product of cellular respiration.
The main functions of the respiratory system include:
- Gas exchange: Facilitating the exchange of O2 and CO2 between the blood and the air
- Regulation of blood pH: Maintaining the pH balance of the blood by controlling the levels of CO2
- Production of sound: Enabling vocalization and speech through the vibration of vocal cords
- Defense against pathogens: Filtering and trapping inhaled particles and pathogens
Anatomy of the Respiratory System
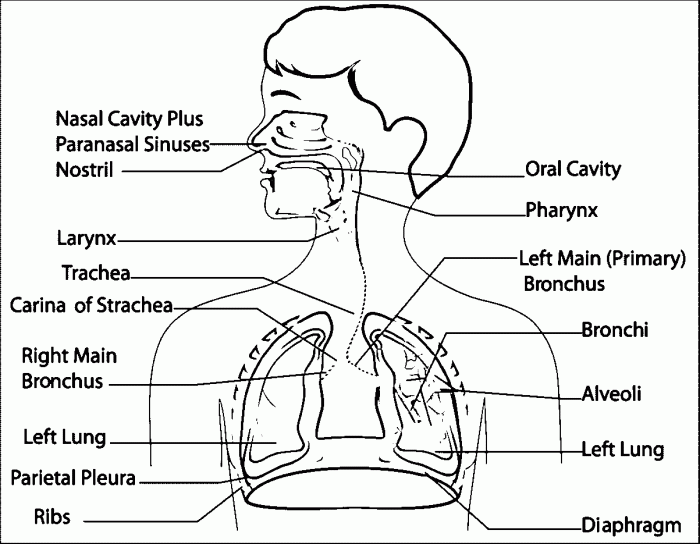
| Organ | Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Nose and nasal cavity | Warming, filtering, and moistening inhaled air; olfaction | Upper face |
| Pharynx | Passageway for air and food; assists in swallowing | Throat |
| Larynx | Houses the vocal cords; produces sound | Neck |
| Trachea | Conducts air to and from the lungs; lined with ciliated cells | Chest |
| Bronchi | Branching airways that carry air into the lungs | Chest |
| Bronchioles | Smaller airways that lead to the alveoli | Lungs |
| Alveoli | Thin-walled sacs where gas exchange occurs | Lungs |
Nose and Nasal Cavity
The nose and nasal cavity serve as the initial point of entry for inhaled air. The nasal hairs and mucus trap dust, pollen, and other particles, while the blood vessels in the nasal cavity warm and moisten the air.
Pharynx
The pharynx, commonly known as the throat, is a muscular tube that connects the nasal cavity and mouth to the larynx and esophagus. It serves as a passageway for both air and food.
Larynx, Respiratory system worksheet answer key
The larynx, also known as the voice box, contains the vocal cords. When air passes through the larynx, the vocal cords vibrate, producing sound.
Trachea
The trachea, or windpipe, is a long, tube-like structure that conducts air to and from the lungs. Its inner lining is covered with ciliated cells that help remove mucus and debris.
Bronchi
The trachea branches into two main bronchi, which enter the lungs. The bronchi continue to branch into smaller and smaller airways, eventually leading to the alveoli.
Bronchioles
Bronchioles are the smallest airways in the respiratory system. They are lined with smooth muscle, which can constrict or relax to adjust airflow.
Alveoli
Alveoli are tiny, thin-walled sacs where gas exchange occurs. They are surrounded by capillaries, allowing for the efficient exchange of O2 and CO2 between the blood and the air.
Questions and Answers: Respiratory System Worksheet Answer Key
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
The primary function of the respiratory system is to facilitate the exchange of gases between the body and the external environment, specifically the intake of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide.
What are the main organs of the respiratory system?
The main organs of the respiratory system include the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli.
How does the diaphragm contribute to respiration?
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts, flattening and moving downward, which increases the volume of the thoracic cavity and draws air into the lungs.