Figure walkthrough using recombinant dna technology to make useful products – Figure Walkthrough: Harnessing Recombinant DNA Technology for Useful Product Creation delves into the captivating world of genetic engineering, exploring the transformative power of recombinant DNA technology in crafting valuable products that address real-world challenges.
Recombinant DNA technology has revolutionized various fields, from medicine and agriculture to industrial biotechnology, offering unprecedented opportunities to create innovative solutions. This figure walkthrough provides a step-by-step guide to understanding the principles, applications, and ethical considerations surrounding this groundbreaking technology.
Recombinant DNA Technology Overview
Recombinant DNA technology involves combining genetic material from different sources to create new DNA molecules. It offers numerous applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
Key Components and Processes
- Restriction enzymes:Cut DNA at specific sequences.
- DNA ligase:Joins DNA fragments together.
- Plasmids:Small, circular DNA molecules used as vectors to carry foreign DNA.
- Host organisms:Bacteria or yeast that replicate and express recombinant DNA.
Applications
- Production of therapeutic proteins (e.g., insulin, growth hormone)
- Development of genetically modified crops (e.g., pest resistance, drought tolerance)
- Creation of diagnostic tools (e.g., DNA fingerprinting, genetic testing)
Creating Useful Products Using Recombinant DNA Technology
Types of Products, Figure walkthrough using recombinant dna technology to make useful products
- Therapeutic proteins:Hormones, enzymes, and antibodies used to treat diseases.
- Genetically modified organisms (GMOs):Plants or animals with altered genetic material for improved traits.
- Diagnostic tools:DNA probes and primers used to identify and analyze genetic material.
Advantages
- Production of large quantities of proteins and other products.
- Modification of organisms to improve traits or create new ones.
- Development of diagnostic tools for early detection and personalized medicine.
Disadvantages
- Potential risks of introducing foreign genes into organisms.
- Ethical concerns regarding the modification of living beings.
- Regulatory challenges and public acceptance issues.
Figure Walkthrough: A Step-by-Step Guide
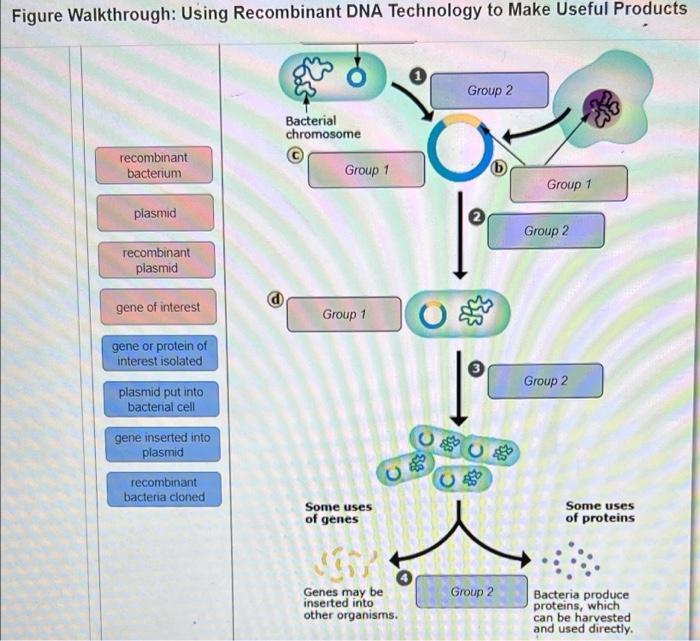
| Step | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Isolate DNA | Extract DNA from the desired source (e.g., bacteria, plant, human). |
| 2. Cut DNA | Use restriction enzymes to cut DNA at specific sequences. |
| 3. Insert foreign DNA | Ligate the foreign DNA into the cut DNA using DNA ligase. |
| 4. Transform host organism | Introduce the recombinant DNA into a host organism (e.g., bacteria) for replication. |
| 5. Screen for transformants | Identify host organisms that have successfully taken up the recombinant DNA. |
| 6. Culture and harvest product | Grow the transformants and harvest the desired product (e.g., protein, GMO). |
Ethical Considerations: Figure Walkthrough Using Recombinant Dna Technology To Make Useful Products
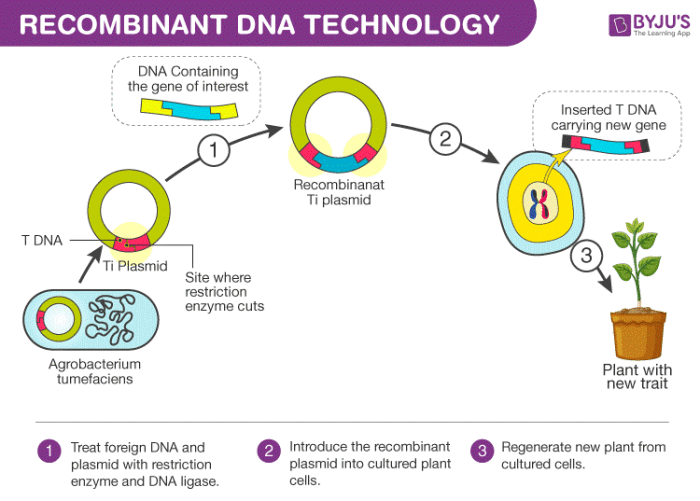
Potential Risks
- Unintended effects on the environment or human health.
- Creation of new pathogens or resistant organisms.
- Genetic pollution through the transfer of genes between organisms.
Potential Benefits
- Development of cures for diseases and improved medical treatments.
- Increased food production and improved crop yields.
- Advancements in scientific research and understanding of genetics.
Ethical Dilemmas
- The use of human embryos in research.
- The patenting of genetically modified organisms.
- The release of GMOs into the environment.
Future Directions
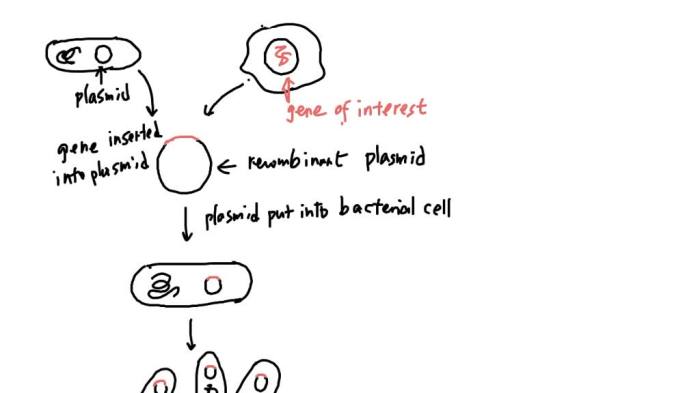
Potential Advancements
- Development of gene editing technologies (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9) for precise genome modifications.
- Creation of synthetic biology systems for designing and building new biological systems.
- Application of recombinant DNA technology in regenerative medicine and personalized medicine.
Areas of Impact
- Healthcare: Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases.
- Agriculture: Sustainable food production, crop improvement, and biofuels.
- Environment: Bioremediation, conservation, and biodiversity protection.
Question Bank
What are the key advantages of using recombinant DNA technology?
Recombinant DNA technology offers numerous advantages, including the ability to create precise genetic modifications, enhance product quality and yield, and develop novel therapies and diagnostics.
Are there any ethical concerns associated with recombinant DNA technology?
While recombinant DNA technology has immense potential, it also raises ethical considerations related to gene editing, intellectual property rights, and potential environmental impacts. Responsible use and regulation are crucial to ensure its safe and ethical application.