Welcome to the Age of Rock and Plate Tectonics Quiz! Embark on a captivating exploration of the geological era that shaped our planet. This quiz delves into the fundamental concepts of plate tectonics, its key processes, and its profound impact on life and evolution.
Throughout Earth’s history, the movement of tectonic plates has played a pivotal role in shaping its surface, creating diverse landscapes, influencing climate patterns, and driving the evolution of life. Discover the geological evidence that supports the theory of plate tectonics, and explore its ongoing implications for the Earth’s ecosystems and geological hazards.
Age of Rock and Plate Tectonics: Age Of Rock And Plate Tectonics Quiz
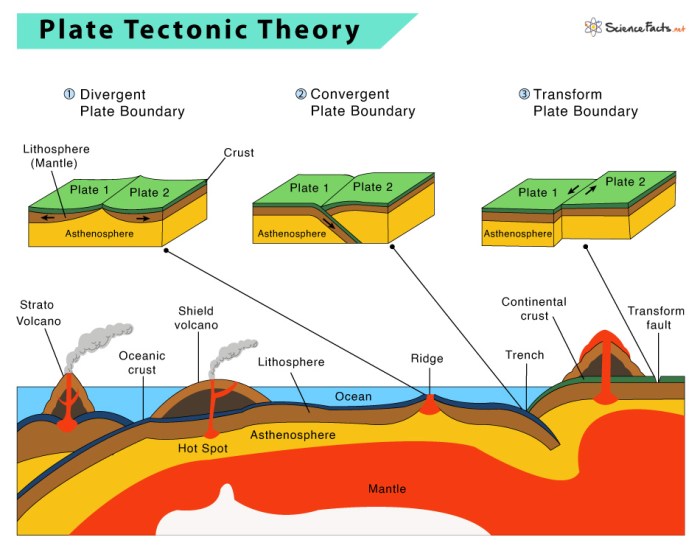
The “age of rock and plate tectonics” refers to a geological era spanning from the formation of the Earth’s crust to the present day. This era is characterized by the movement and interaction of Earth’s tectonic plates, which are large, rigid pieces of the Earth’s lithosphere.
Plate tectonics is the primary mechanism by which the Earth’s surface has been shaped over time.
Key Processes and Events, Age of rock and plate tectonics quiz
Plate tectonics involves several key processes, including:
- Subduction:When one tectonic plate moves beneath another, causing the denser plate to sink into the mantle.
- Spreading:When two tectonic plates move apart, creating new crustal material.
- Collision:When two tectonic plates collide, causing one or both plates to buckle and fold.
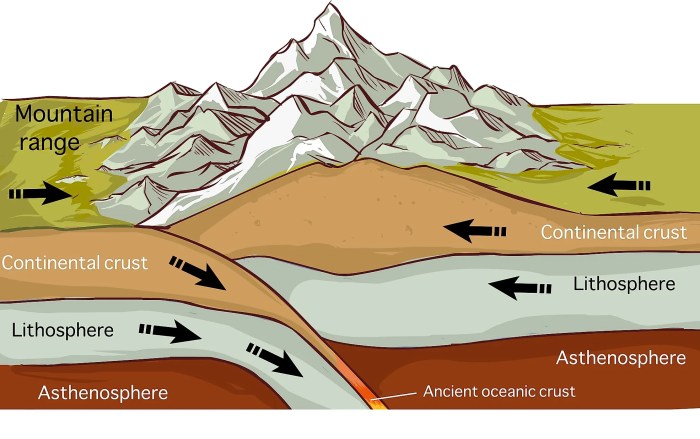
Significant geological events that occurred during the “age of rock and plate tectonics” include the formation of mountain ranges, the opening and closing of ocean basins, and the creation of new landmasses. These events have played a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s surface and creating the diverse landscapes we see today.
Impacts on Life and Evolution
Plate tectonics has significantly influenced the evolution of life on Earth. The formation of new landmasses and changes in climate caused by plate movements have impacted the distribution and diversification of species. For example, the collision of the Indian and Asian plates created the Himalayan mountain range, which acted as a barrier to species migration and led to the evolution of distinct species on either side of the mountains.
Geological Evidence
The theory of plate tectonics is supported by various types of geological evidence, including:
- Fossils:The distribution of fossils of the same species on different continents suggests that these continents were once connected and have since drifted apart.
- Rock formations:The presence of similar rock formations on different continents indicates that they were once part of the same tectonic plate.
- Magnetic anomalies:The Earth’s magnetic field is recorded in rocks, and the patterns of these anomalies provide evidence for the movement of tectonic plates over time.
Current and Future Implications
Plate tectonics continues to impact the Earth’s surface today. The movement of tectonic plates causes geological hazards such as earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. It also influences the distribution of natural resources and shapes the Earth’s ecosystems. Understanding plate tectonics is essential for predicting and mitigating these hazards and for managing the Earth’s resources sustainably.
Top FAQs
What is the significance of the Age of Rock and Plate Tectonics?
The Age of Rock and Plate Tectonics marks a period in Earth’s history characterized by the formation of the first solid rocks and the initiation of plate tectonic processes. These processes have shaped the Earth’s surface, creating mountains, oceans, and continents, and driving the evolution of life.
How do plate tectonics influence the distribution of life on Earth?
Plate tectonics plays a crucial role in the distribution of life on Earth. The movement of tectonic plates creates new landmasses and changes climate patterns, which in turn impact the distribution and diversification of species. For example, the formation of the Isthmus of Panama connected North and South America, allowing the exchange of species between the two continents.
What are some examples of geological evidence that support the theory of plate tectonics?
Geological evidence supporting plate tectonics includes the distribution of fossils, rock formations, and magnetic anomalies. Fossils of the same species found on different continents indicate that these landmasses were once connected. Rock formations, such as folded and thrust belts, provide evidence of past plate collisions.
Magnetic anomalies in the ocean floor align with the boundaries of tectonic plates, indicating their movement over time.